- What is the most significant flaw in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
- What are the distinctions between Maslow and Herzberg’s theories?
- What are the distinctions between the ERG and Maslow theories in terms of how people can climb up the hierarchy to meet their needs?
- What is the problem with Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
- What are the drawbacks of a hierarchical structure?
- What is the most significant flaw in Maslow’s humanistic theory?
- What are the distinctions between Herzberg’s motivating and sustaining factors?
- In Herzberg’s hypothesis, what is the hygiene factor?
- What is the concept of motivation, and how do Maslow’s and Herzberg’s theories of motivation compare and contrast with real-life examples?
- Why are Maslow’s needs structured in a hierarchical order?
- In Maslow’s hierarchy of needs model, what is the correct order of importance from lowest to highest?
- In your own life, how would you use Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
- What is Maslow’s motivation theory?
- Do you agree with Maslow’s hierarchy of needs or disagree with it?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of a hierarchical structure?
- What are some of the drawbacks of using a hierarchical database model?
- What is the most important drawback of the hierarchy principle?
- What are some of the humanistic theory’s flaws?
- What are three flaws in the humanistic viewpoint?
- What are some of the drawbacks of humanism?
- What is the main critique of Herzberg’s two-factor motivation model? Do you believe it contributes to a better understanding of workplace motivation?
- How does Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory influence an individual’s behavior?
- What significance does Herzberg’s two-factor hypothesis have?
- What are Herzberg’s theoretical limitations?
- How do you apply Herzberg’s motivation theory?
- In Herzberg’s motivation theory, what are the two aspects of motivation?
- In Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, which needs are hygiene factors?
- What are the similarities and differences between Maslow’s and Herzberg’s theories?
- What can we learn about people’s needs from Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
- In Maslow’s hierarchy, which of the following is a lower order need?
- In Maslow’s hierarchy of requirements, which of the following is not a level?
What is the most significant flaw in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
Maslow’s hierarchy-of-needs theory has a key flaw: it can’t be objectively tested because there’s no way to know how satisfied one level of need must be before the next higher need kicks in.
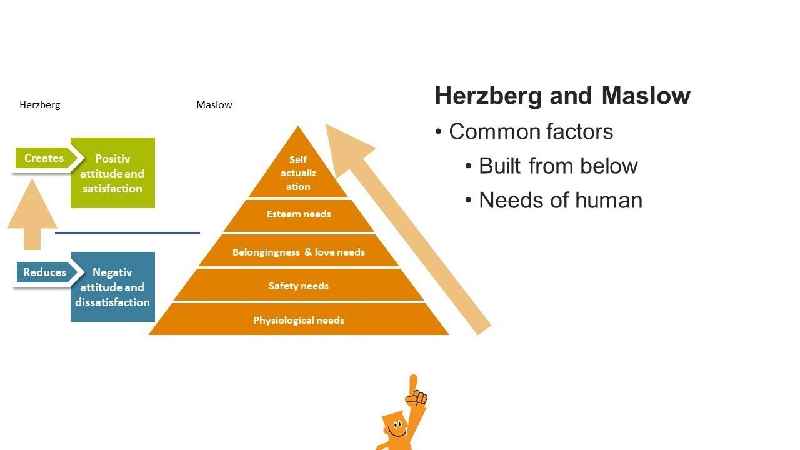
What are the distinctions between Maslow and Herzberg’s theories?
Differences between Maslow’s and Herzberg’s theories of motivation are crucial. Maslow’s theory is descriptive, but Herzberg’s theory is straightforward and prescriptive. Maslow’s thesis is based on human needs and how they are met. Herzberg’s idea, on the other hand, is based on reward and recognition.
What are the distinctions between the ERG and Maslow theories in terms of how people can climb up the hierarchy to meet their needs?
Maslow’s Theory and the ERG Theory: What’s the Difference? In other words, according to Maslow’s theory, everyone’s requirements develop via a five-level pyramid structure, whereas according to the ERG theory, people meet their needs in different ways at different levels.
What is the problem with Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
According to Maslow’s famous Hierarchy of Needs, humans require food, shelter, and warmth in order to exist. uCLA professor and social neuroscience researcher Matthew Lieberman, on the other hand, believes Maslow was mistaken. Our basic human requirements do not include food, shelter, or warmth.
What are the drawbacks of a hierarchical structure?
Power concentration is a disadvantage. Power and authority are concentrated at the greatest levels feasible in hierarchical institutions.
What is the most significant flaw in Maslow’s humanistic theory?
One of the most common criticisms leveled towards humanistic psychology is that its notions are too hazy. Subjective ideas like true and real experiences, critics contend, are impossible to objectify; an event that is real for one person may not be real for another.
What are the distinctions between Herzberg’s motivating and sustaining factors?
Company policy, compensation, employment security, position, working conditions, and other elements are examples of maintenance factors. Motivational variables, on the other hand, are linked to job features. The presence of these, or a rise in them, satisfies people and enhances efficiency; nevertheless, their removal or reduction does not dissatisfy.
In Herzberg’s hypothesis, what is the hygiene factor?
Extrinsic characteristics of the work environment, such as business policy, interactions with supervisors, working conditions, relationships with peers and subordinates, income and benefits, and job security, are what Herzberg referred to as hygiene factors (also known as dissatisfiers).
What is the concept of motivation, and how do Maslow’s and Herzberg’s theories of motivation compare and contrast with real-life examples?
Conclusion. The key distinction is that Maslow’s theory is based on human wants and their satisfaction. Herzberg’s idea, on the other hand, is based on reward and recognition.
Why are Maslow’s needs structured in a hierarchical order?
What Is Maslow’s Needs Hierarchy? Maslow believed that human wants may be structured into a hierarchy in order to better understand what motivates people. When a lower need is met, the following need in the hierarchy becomes our center of attention, according to Maslow.
In Maslow’s hierarchy of needs model, what is the correct order of importance from lowest to highest?
Maslow arranged human needs into a pyramid that comprises physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization requirements (from lowest to highest level).
In your own life, how would you use Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
Physiological (food and clothes), safety (job security), love and belonging needs (friendship), esteem, and self-actualization are the needs from the bottom of the hierarchy up. Individuals must attend to lower-level demands before they can attend to higher-level requirements.
What is Maslow’s motivation theory?
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a motivation theory that argues that an individual’s conduct is dictated by five categories of human needs. Physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs are some of these needs.
Do you agree with Maslow’s hierarchy of needs or disagree with it?
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is popular and generally well-accepted, however the available evidence does not always back up Maslow’s theory. Although the hypothesis is commonly held, there is little evidence to back it up.
What are the benefits and drawbacks of a hierarchical structure?
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of a Hierarchical Structure?
- Clear Chain of Command is an advantage.
- Clear Paths to Success are an advantage.
- Specialization is an advantage.
- Poor flexibility is a disadvantage.
- Communication Barriers are a disadvantage.
- Organizational Disunity is a disadvantage.
What are some of the drawbacks of using a hierarchical database model?
The hierarchical approach is appropriate for simple structures, but it only supports one-to-many relationships. Other disadvantages of the hierarchical database model include: Because of the tree-like structure, data must be stored repeatedly in many separate entities.
What is the most important drawback of the hierarchy principle?
The most important downside of this method is the time delay.
What are some of the humanistic theory’s flaws?
One of the most common criticisms of humanistic psychology is that its notions are overly broad. Subjective ideas like authentic and realexperiences, critics contend, are impossible to objectify; an experience that is actual for one person may not be real for another.
What are three flaws in the humanistic viewpoint?
Humanistic psychology has been criticized for its subjectivity (non-scientific descriptions such as the spontaneity of self-actualized people, which are based on the theories ideals), and the centrality on individualism. According to some psychologists, focusing too much on our own goals…
What are some of the drawbacks of humanism?
Disadvantages.
- It is overly optimistic when it comes to human behavior, implying that people are intrinsically good and would pick great routes for their lives. However, some people’s free will and choices are limited.
- It’s difficult to examine since there’s too much emphasis on subjective experience.
What is the main critique of Herzberg’s two-factor motivation model? Do you believe it contributes to a better understanding of workplace motivation?
The Herzberg Two-Factor Theory has been criticized. Another critique is that the Two Factor Theory presupposes that better production equals higher job happiness. There are many reasons to disagree, such as external influences that could affect production.
How does Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory influence an individual’s behavior?
According to Herzberg, hygiene issues cannot excite employees but might reduce unhappiness if managed appropriately. In other words, they can only cause dissatisfaction if they are not present or if they are mistreated. Company policies, supervision, remuneration, interpersonal interactions, and working environment are all examples of hygiene topics.
What significance does Herzberg’s two-factor hypothesis have?
According to Herzberg’s two-factor theory, employers cannot choose between motivation and hygiene, but must work to improve both. Employers can adjust company policies to boost staff welfare, avoiding low motivation and poor cleanliness at the same time.
What are Herzberg’s theoretical limitations?
Two-Factor Theory’s Limitations
- Situational variables are ignored by the two-factor framework.
- Herzberg assumed there was a link between happiness and production.
- The theory’s validity is debatable.
- There was no comprehensive satisfaction metric employed.
How do you apply Herzberg’s motivation theory?
How to Apply Herzberg’s Theory
- Reevaluate the company’s weak policies.
- All employees should be supervised in a way that is both effective and supportive.
- Encourage a respectful work environment for all employees.
- Provide wages that are competitive.
- By taking on significant work duties, you can help to improve your job standing.
- Ensure that your work is secure.
In Herzberg’s motivation theory, what are the two aspects of motivation?
Motivators and hygiene factors are the two factors established by Herzberg.
- Factors that Motivate. Employees work harder when there are motivators present. They can be discovered within the scope of the job.
- Factors affecting hygiene. Employees will work less hard if hygiene considerations are absent.
In Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, which needs are hygiene factors?
Company policy, supervision, interpersonal relations, working circumstances, and remuneration, he argued, are hygiene issues rather than motivators. According to the notion, job unhappiness might be caused by a lack of hygienic aspects, but their presence does not inspire or produce satisfaction.
What are the similarities and differences between Maslow’s and Herzberg’s theories?
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory and Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory have some similarities. Both models are unable to account for individual variances in motivation. Both models are based on content. They concentrate on discovering demands that compel people to act.
What can we learn about people’s needs from Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
One of the most well-known theories of motivation is Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. According to Maslow’s hypothesis, our activities are driven by physiological requirements. It’s commonly depicted as a need pyramid, with the most fundamental demands at the bottom and more sophisticated needs at the top.
In Maslow’s hierarchy, which of the following is a lower order need?
The lowest level of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is physiological needs. They are the most important things a person can have in order to live. Shelter, water, food, warmth, rest, and health are just a few of them.
In Maslow’s hierarchy of requirements, which of the following is not a level?
As a result, individualism and collectivism cannot be found in Maslow’s hierarchy of requirements.
Category:Hygiene & Toiletries